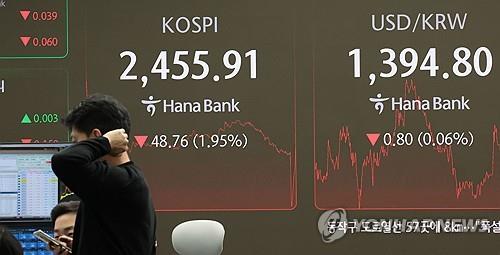
Seoul Stock Market Faces Turbulence: Analyzing the 2% Decline Amid Economic Concerns
The Seoul Stock Exchange has recently experienced a sharp decline of 2%, sparking significant concern among investors and market analysts. This drop comes as South Korea grapples with a variety of economic challenges, both domestic and global. The question on many minds is whether this downturn is a temporary blip or an indication of deeper, more persistent issues that could ripple through the global market. In this article, we explore the reasons behind the current market turbulence, the broader economic factors at play, and the potential implications for South Korea’s economy and the international financial landscape.
Understanding the 2% Drop: A Brief Overview
On [insert date], the Seoul Stock Exchange saw a significant dip, closing 2% lower than its previous day’s performance. This drop comes at a time of heightened uncertainty, with several macroeconomic factors contributing to the unsettling market conditions. At first glance, this decline might seem like a short-term reaction to isolated events, but a closer examination reveals a confluence of risks that are weighing on investors’ confidence.
Key Factors Behind the Market Decline
Several critical issues have converged, leading to the sharp drop in South Korea’s stock market. Let’s explore the main factors behind the turbulence:
1. Slowing Economic Growth in South Korea
South Korea’s economy, which has long been one of the most robust in Asia, has recently shown signs of slowing. The country’s GDP growth forecast for the year has been revised downward, with many analysts predicting growth rates below 2%. This slowdown is largely attributed to decreased consumer spending, stagnating exports, and weaker-than-expected industrial output. The slowing demand for South Korean technology products, including semiconductors, which account for a significant portion of the country’s exports, has been particularly impactful.
2. Global Economic Pressures
The South Korean market is also feeling the ripple effects of broader global economic challenges. The ongoing trade tensions between major economies, such as the United States and China, have created a climate of uncertainty. As the U.S. Federal Reserve continues to tighten monetary policy, concerns about potential recessions in both developed and emerging markets are weighing on investor sentiment. Additionally, inflationary pressures remain a global issue, particularly in key South Korean trading partners like the U.S. and the European Union.
3. Rising Interest Rates and Inflation
One of the most significant macroeconomic challenges is the rise in global interest rates. The Bank of Korea has raised interest rates multiple times in the past year in an attempt to combat inflation, which has remained stubbornly high despite efforts to control it. Higher borrowing costs are discouraging investment and consumer spending, further stalling economic growth. This is particularly troublesome for South Korea, where household debt levels are among the highest in the OECD. With inflation rates hovering around [insert number]%, many households are feeling the pinch, which in turn is reducing domestic consumption.
4. Geopolitical Risks in the Region
The geopolitical climate in East Asia remains tense, with ongoing concerns over North Korea’s missile tests and its aggressive posture toward South Korea and the U.S. These tensions create an atmosphere of uncertainty, which is often reflected in financial markets. Moreover, the ongoing U.S.-China rivalry continues to influence the region’s economic dynamics, particularly in terms of trade routes and supply chains. Investors tend to become more risk-averse when geopolitical instability rises, leading to a sell-off in equities.
5. Weak Corporate Earnings
Many of South Korea’s largest companies, particularly in the technology and manufacturing sectors, have reported disappointing earnings for the past quarter. Samsung Electronics, one of the nation’s flagship companies, reported a sharp decline in profits due to weaker demand for its semiconductor products. This downturn in corporate performance has led to a broader loss of investor confidence, contributing to the sell-off in stocks.
The Implications for South Korea’s Economy
The decline in the Seoul Stock Market is not just a stock market event—it is a reflection of broader economic trends that could have significant implications for South Korea’s economy in the medium to long term.
1. Impact on Consumer Confidence
A sustained drop in the stock market can undermine consumer confidence, particularly among middle-class South Koreans who have a significant portion of their wealth tied up in equities. If individuals see their investments diminish, they may reduce their spending, further dampening economic growth. This is a critical issue, as South Korea’s consumer-driven economy depends heavily on domestic consumption.
2. Increased Risk of Recession
The 2% drop in the stock market might be an early warning sign of a potential recession. If the economic slowdown continues, South Korea may face higher unemployment rates, lower corporate investments, and a slowdown in manufacturing activity. Given the country’s reliance on exports, any prolonged downturn in global demand could exacerbate these effects.
3. Impact on Global Markets
South Korea’s economy is intricately tied to the global supply chain, particularly in the semiconductor, automotive, and shipbuilding industries. A slowdown in South Korea’s economy could have ripple effects throughout Asia and beyond. For instance, if South Korea’s semiconductor production is curtailed, companies in the U.S., Japan, and China may experience supply shortages. As one of the largest economies in Asia, South Korea’s economic challenges are of global concern, especially for investors with exposure to emerging markets.
What Lies Ahead: Possible Solutions and Projections
Experts have pointed to several possible solutions that could help stabilize the situation and prevent further declines in the market.
1. Fiscal Stimulus Measures
The South Korean government may implement fiscal stimulus packages to boost economic activity. This could include increased public spending on infrastructure projects, tax breaks for businesses, or direct financial support to households. Such measures could help revive consumer demand and stabilize the job market, which would, in turn, support the stock market.
2. Structural Reforms in Key Sectors
South Korea could also benefit from structural reforms aimed at increasing productivity and fostering new sources of growth. For instance, investing in green technologies, artificial intelligence, and biotechnology could help diversify the economy and reduce dependence on traditional industries like semiconductors and heavy manufacturing. Additionally, streamlining regulations and enhancing labor market flexibility could attract more foreign investment.
3. Strengthening Trade Relations
Another avenue for growth is strengthening South Korea’s trade relations with key partners. Diversifying its export markets, especially in emerging economies, could help mitigate the effects of any downturn in traditional markets like China or the U.S. Expanding South Korea’s role in regional trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), could also offer new opportunities for economic expansion.
Conclusion: A Turning Point for South Korea?
The 2% decline in Seoul’s stock market has brought to light a series of economic challenges that South Korea must address. While the market’s volatility is concerning, it also serves as a reminder of the interconnectedness of global economies and the fragility of investor sentiment in times of uncertainty. Whether this decline is temporary or part of a larger trend remains to be seen. However, policymakers and businesses must act swiftly and decisively to manage risks and stimulate economic growth. South Korea’s path forward will depend on how it navigates these turbulent waters and adapts to the rapidly changing global economic landscape.
For more insights on how global economic trends are influencing local markets, visit IMF South Korea Overview.
See more CNBC Network